Index
Le peripheral retinal degenerations are areas of the peripheral retina that present a particular structural fragility. These areas occur more frequently in people with high myopia due to the progressive elongation of the eyeball which, over the years, determines thinning and fragility of the retina.
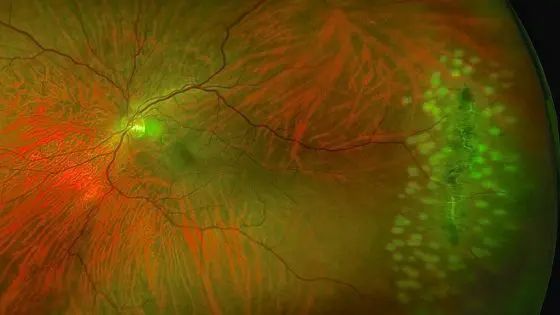
Types of peripheral retinal degenerations
There are several types of peripheral retinal degenerations: the latex degeneration, with well-defined areas of thinning, whitish in color and generally oval in shape; there snail slime degeneration, with numerous white-silvery dots arranged in such a way as to recall the slime of a snail; there retinoschisis, with separation of the peripheral retina into two sheets; there paving degeneration, with areas of atrophy that reveal the choroid and its underlying vessels.
All of these different types of peripheral retinal degenerations lead to an increased risk of retinal tears need retinal detachment, particularly in people who play particularly intense sports and in people over 45-50 years of age, in whom the vitreous body it begins to contract causing a traction on the retina which in normal conditions tends to resolve itself but in the presence of peripheral retinal degenerations it can more easily create retinal breaks and, consequently, a retinal detachment.
Symptoms
People with peripheral retinal degenerations do not have specific symptoms unless the degenerations increase to the point of interfering with the peripheral visual field or the vitreous does not exert tractions on the peripheral retina such as to cause retinal ruptures.
When retinal breaks are created, usually there is the perception of bright flashes (photopsies). In these cases, an eye examination must be requested with extreme urgency to avoid the danger of retinal detachment, an extremely dangerous event for the vision.
Diagnosis
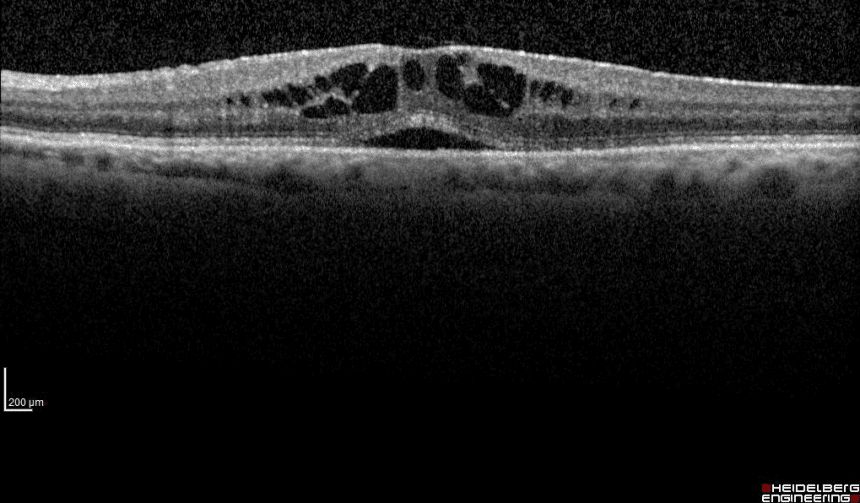
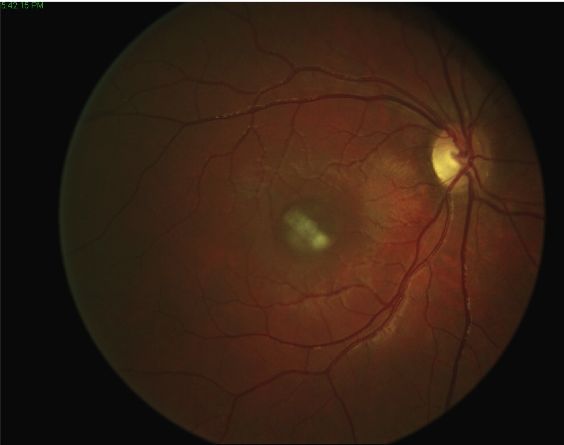
Retinal tears can be highlighted with specific instrumental examinations such as optical coherence tomography (OCT) high resolution, able to analyze in detail the cell layers that make up the retinal tissue, theB-Scan ultrasound, to evaluate possible tractions on the retina by the vitreous, and the wide field retinography, to verify the structural integrity of the peripheral retina.
These tests are particularly recommended for very short-sighted people and for people over the age of 40-45, particularly if they play very intense sports.
Treatment
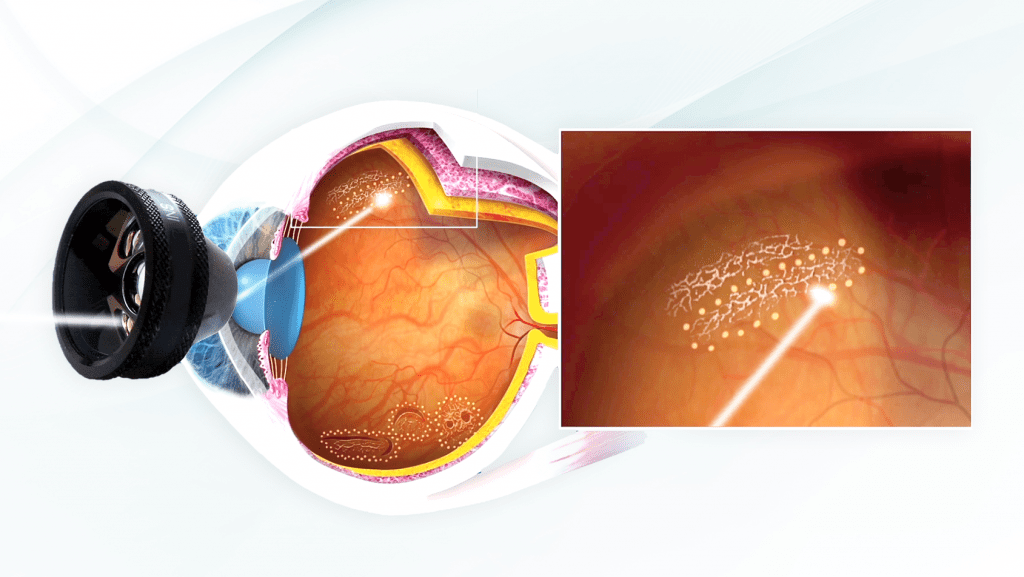
In the presence of peripheral retinal degeneration it is usually advisable to use a photocoagulative laser treatment.
This treatment uses a duplicate frequency laser and is performed in a few minutes, after administering a mydriatic eye drops to dilate the pupil, to allow the specialist to visualize the retinal periphery, and a anesthetic eye drops, to facilitate the application of a rigid wide-angle contact lens, necessary to be able to apply the laser.
The treatment creates "scars" around the retinal areas at risk, in order to isolate retinal degeneration and prevent its progression. In this way, a "laser barrage”Able to prevent any retinal tears and retinal detachment that these could cause.
Pathology and treatment on video
Do you need more information?
Do not hesitate to contact me for any doubt or clarification. I will evaluate your problem and it will be my concern and that of my staff to answer you as quickly as possible.