Index
Redness, tearing, feeling of sand in the eyes? It could be conjunctivitis.
Conjunctivitis is inflammation or infection of the conjunctiva, a thin transparent membrane that lines a large part of the anterior surface of the eye.
Conjunctivitis can affect adult patients, but also the smallest ones and must be dealt with promptly to avoid the onset of complications that can sometimes become difficult to eradicate.
What are the possible causes?
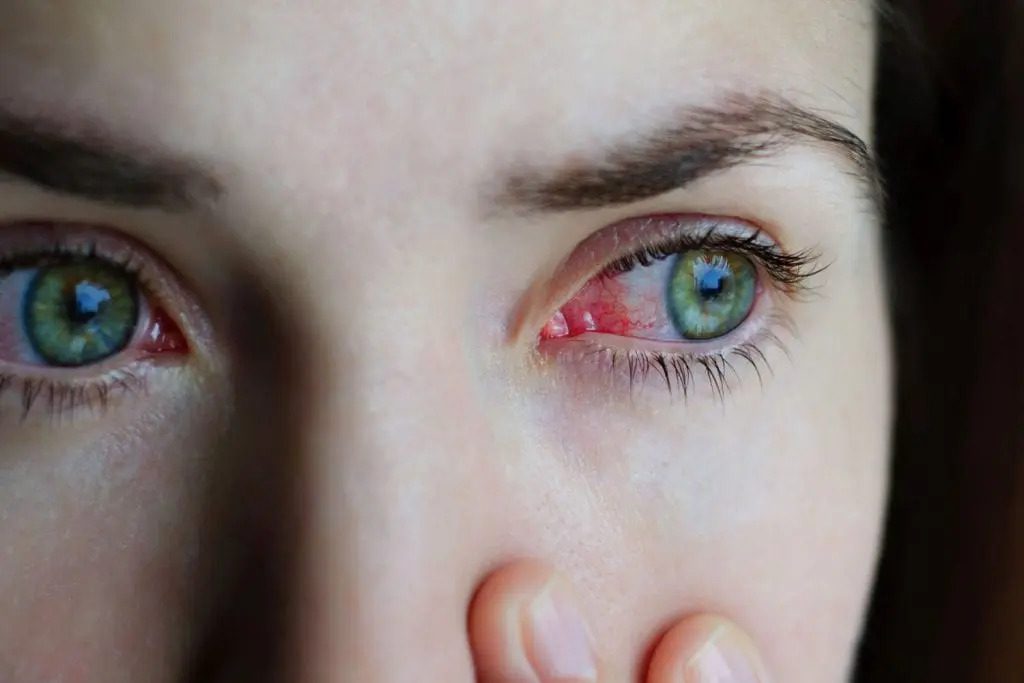
There are several: allergic, infectious (viral, bacterial or neonatal ophthalmia), from chemical irritants (shampoos, cosmetics) or foreign bodies (contact lenses).
Allergic forms occur mainly in subjects who have basic allergies and therefore, in addition to the visual apparatus, they often also have systemic involvement (respiratory tract or skin).
They are due to an allergic reaction to irritants such as dust or pollen. These forms are not contagious to others and can be seasonal or perennial, depending on the irritant involved. When the allergen comes into contact with the conjunctiva, which is rich in blood vessels and mast cells, the latter release histamines and other inflammatory substances, causing inflammation of the conjunctiva.
Infectious forms are usually viral or bacterial. Viral ones are particularly contagious and caused by viruses dispersed in the air, often associated with colds and which can therefore be easily transmitted by sneezing, coughing or touching the eyes with contaminated surfaces. The bacterial ones, caused by various types such as staphylococcus or streptococcus, are also contagious and are transmitted more frequently from one individual to another through an eye-hand-eye contact mode; Neonatal ophthalmia (neonatal conjunctivitis) is a serious bacterial infection that the newborn can develop within 30 days of birth: the baby contracts the infection when passing through the birth canal due to the presence of chlamydia or gonorrhea and can lead to permanent visual damage . Chlamydial infections represent a minor but not negligible entity that can occasionally be contracted as well as sexually even in the pool. Conjunctivitis caused by fungi and fungi are particularly rare and generally occur following trauma or in immunosuppressed subjects.
What are the symptoms?
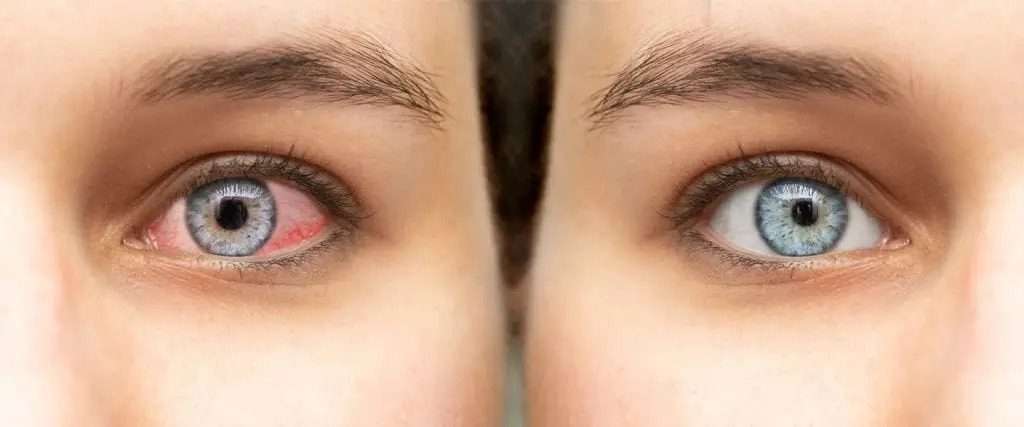
Patients with conjunctivitis have common symptoms:
- redness in one or both eyes
- burning
- feeling of sand
- photophobia
- lacrimation (especially in viral infections)
- sticky, yellowish discharge (bacterial infections)
- watery eyes, with swollen eyelids and a runny nose (allergic conjunctivitis)
How to treat them?
The treatment of conjunctivitis varies according to the causative agent, in all forms, however, the patient may find it beneficial to carry out compresses with hot water.
In the case of allergic conjunctivitis, the first step is to remove or limit exposure to the allergen.
Artificial tears may be prescribed initially while, in cases where the clinical picture is more evident, antihistamine or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory (NSAID) eye drops to relieve symptoms. Mast cell membrane stabilizers that release histamine also represent a valid therapeutic aid.
Viral conjunctivitis due to adenovirus and also epidemic, highly contagious, has a spontaneous resolution like common colds, no specific medication is generally needed, they do not respond to antibiotic eye drops and normal ocular condition will be restored within 2/3 weeks. Artificial tears may possibly be prescribed as supportive therapy to decrease the sensation of ocular discomfort that accompanies its course. In the presence of Herpes viral conjunctivitis, it is instead necessary to promptly establish local or systemic antiviral therapy to eliminate the risk of possible lesions which, if not treated, can cause permanent corneal opacification and such as to require a lamellar corneal transplant or at all. thickness.
Antibiotic eye drops are usually prescribed for bacterial conjunctivitis as they help to accelerate the healing process, already evident after 3-4 days from the start of therapy, and to decrease the incidence of possible corneal complications thus preserving visual function.
In the case of chemical conjunctivitis, careful and prolonged washing of the eyes is recommended, but if the contact occurs with alkali or substances that can cause serious chemical injuries and consequent scars, it is essential to immediately contact your trusted ophthalmologist or an emergency room to avoid leaks. important visuals that would then require a corneal transplant often with a high risk of failure due to the significant alterations of the anatomical substrate.
In any case, it is possible and advisable to adopt simple but efficient precautionary measures to avoid the onset of conjunctivitis. First of all, constantly carry out good daily hygiene, avoiding touching your eyes with your hands, washing your hands often, never using other cosmetic products or objects and paying particular attention to the correct use of contact lenses, avoiding gold in the first place. contact with the water of the shower, the pool and the sea.

