Index
Open angle glaucoma is the most common form of glaucoma, it is a progressive and rather slow pathology in causing damage to the optic nerve, but still very dangerous, since the patient has no symptoms and is not aware of the progression of the disease to the most advanced stages.
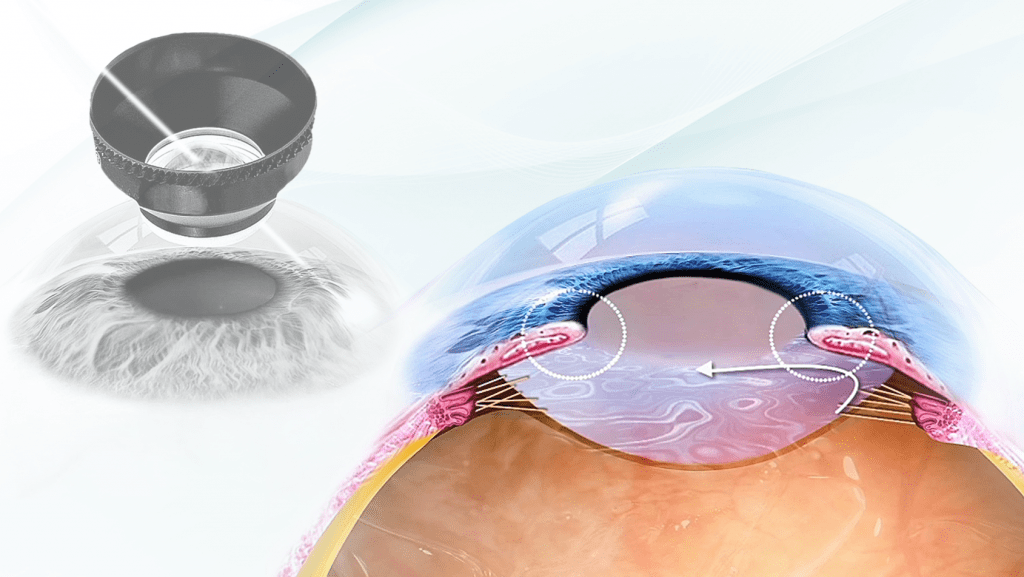
The aqueous humor is a transparent liquid that has the function of nourishing the cornea and crystalline and to eliminate waste products; in a healthy eye, it is continuously produced within the anterior chamber of the eye, by the cells of the non-pigmented epithelium of the ciliary body, and is constantly drained - at the same rate at which it is produced - through an ocular structure called scleral horny trabeculae and other anatomical structures in charge of it.
Thanks to the correct functioning of this physiological mechanism, in a healthy eye the IOP maintains rather constant values ranging between 14 and 21 mmHg.
In patients with open angle glaucoma, the aqueous humor drainage system becomes less and less efficient over time and causes a gradual increase in intraocular pressure (IOP) which progressively damages the optic nerve fibers. This causes a vision deficit which results in a progressive narrowing of the visual field which can evolve with involvement of the central vision up to complete blindness.
Glaucoma is a subtle disease, since the damage progresses slowly, painlessly and asymptomatically and very often, in the absence of regular eye checks, people with this disease perceive its symptoms only when the optic nerve has been severely damaged and the vision is hopelessly impaired.
Advanced glaucoma can be treated, but it cannot be cured, i.e. the lost vision can no longer be recovered, so the prevention , early diagnosis represent the most effective weapon against this dangerous ocular pathology.
Symptoms
Glaucoma progresses slowly and quietly and very often the patient does not have any symptoms specific. In the initial stages, the patient may present mild symptoms that are often not associated with this type of pathology such as view blurred, photophobia and the presence of halos.
In the more advanced stages of the disease, the main symptoms of open angle glaucoma are marked reduction of the peripheral visual field, which can be associated with a serious one reduction of central vision.
We must therefore focus on prevention, which must be carried out through the monitoring of intraocular pressure (IOP) and the maintenance of its values within physiological limits, thanks to the daily administration of some hypotonizing drugs.
Diagnosis
Patients at risk should be monitored regularly with a complete eye examination and instrumental examinations such as Perimetry (computerized or manual), which is used to analyze the total retinal function, both central and peripheral, and the Tomography a Optical Coherence (OCT) at high resolution, which allows you to examine the optic nerve and the retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL, from English Rethinal Nherb FIberian Layer).
Despite the pharmacological treatment, if glaucoma were to evolve and the optic nerve show a progressive suffering, it is necessary to intervene surgically as quickly as possible.
Treatment
Usually the patient suffering from open-angle glaucoma is offered a first therapeutic approach hypotonic drug therapy. This therapy consists of the instillation, several times a day, of hypotensive eye drops.
Although it may seem an easy treatment to carry out, some patients may have some difficulties in respecting the indicated administration times or fail to instill the eye drops correctly.
If this pharmacological procedure does not work either due to poor patient collaboration and insufficient efficacy of the drugs no longer able to reduce intraocular pressure such as to prevent damage to the optic nerve; you opt for two possible named laser procedures Argon laser trabeculoplasty (ALT) or selective laser trabeculoplasty (SLT).
These two laser treatments are painless, they aim to increase the outflow of aqueous humor through theiridocorneal angle and are carried out on an outpatient basis.
Patients suffering from open angle glaucoma who do not respond positively to this type of laser treatment must undergo a surgery called trabeculectomy. The trabeculectomy surgery lasts at least an hour, it can be performed under local or general anesthesia as needed.
Where the therapy does not allow to achieve a decrease in intraocular pressure such as to guarantee, over time, the maintenance of visual function, the use of drain valves (such as Baervelt or Molteno) or a partially destructive intervention of the ciliary body cyclocrio o laser cyclophotocoagulation.
Pathology and treatment on video
Answers to frequently asked questions
What is glaucoma?
Glaucoma is a dangerous eye disease which, if not treated in time, can cause irreversible damage to the optic nerve and consequently to vision.
Why does glaucoma come?
Glaucoma is a multifactorial disease and its onset may depend on a combination of factors such as advanced age, a genetic predisposition and other environmental factors. The most important risk factor for glaucoma is elevated intraocular pressure (IOP).
What is the difference between open angle and angle closure glaucoma?
Open-angle glaucoma is the most frequent form of glaucoma and is a chronic disease that causes progressive and asymptomatic damage to the optic nerve; angle-closure glaucoma, more rare, occurs suddenly, sometimes with warning symptoms such as severe headache, nausea and eye pain, and is able to cause loss of vision in a very short time.
What are the symptoms of glaucoma?
Open angle glaucoma, the most common form of glaucoma, has no symptoms and this characteristic is very dangerous because when the patient notices the first visual impairments it is often too late to block the damage to the optic nerve; for this reason, especially after a certain age, it is advisable to undergo regular eye checks to exclude the presence of this pathology or possibly diagnose it early. Acute angle glaucoma, which is less common, can instead cause warning symptoms such as severe headache, nausea or eye pain.
How is glaucoma treated?
Glaucoma is usually treated pharmacologically by administering eye drops, which can belong to different categories (prostaglandin analogues, carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, beta-blockers and alpha-adrenergic agonists).
How long should you put the glaucoma drops on?
In general, drug therapy for glaucoma must be followed for life, unless there are significant side effects, intolerance or hypersensitivity to the active ingredient or its ineffectiveness.
What should be done if the drops do not lower intraocular pressure?
If the pharmacological therapy proves unsuitable (the patient is unable to put the drops, if he forgets them often, does not tolerate them, has significant side effects or does not benefit from them) laser therapy (laser trabeculoplasty) or surgery (trabeculectomy ).
Do you need more information?
Do not hesitate to contact me for any doubt or clarification. I will evaluate your problem and it will be my concern and that of my staff to answer you as quickly as possible.




