Index
THEhyperopia it's a defect (o error) refractive caused by image focus beyond (behind) the retinal plane. This can be caused by a eyeball too short (in which case we are talking about axial hyperopia) or by a less than normal focusing power of the cornea and/or lens (in which case it's about refractive hyperopia).
Symptoms
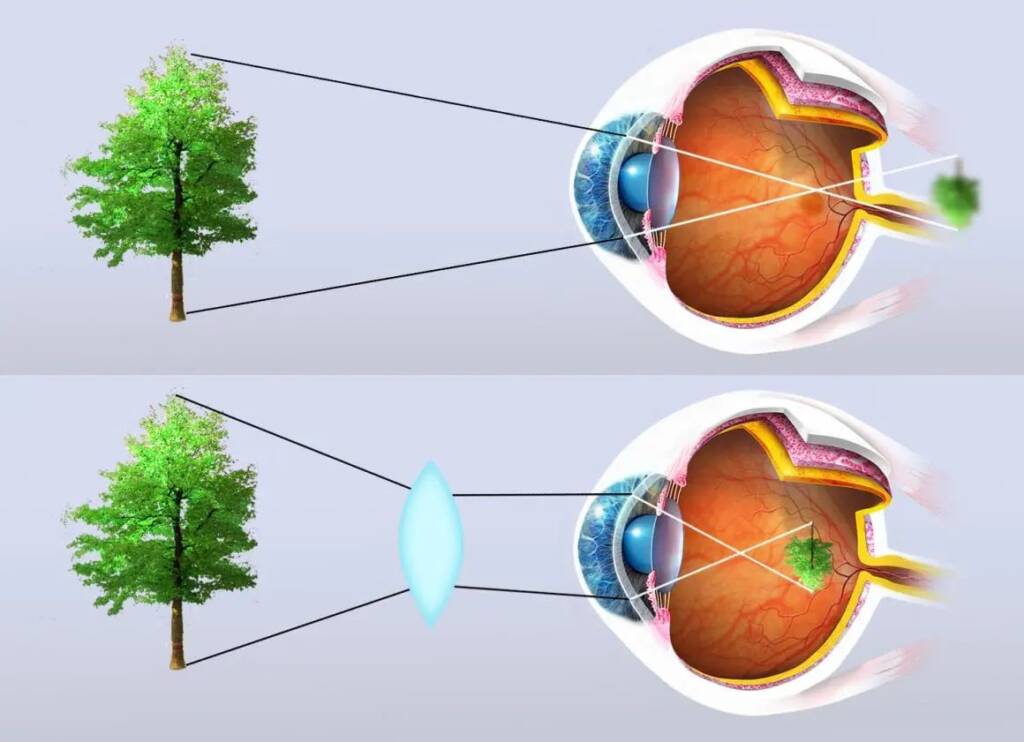
People with mild to moderate farsightedness have difficulty focusing on close objects but see clearly at a distance. For example, as shown in the image, a person with farsightedness of two diopters sees clearly beyond 50 centimeters but blurry below that distance. In the case of axial farsightedness, the eye can compensate for the refractive error for several years thanks to the ability of the crystalline lens to focus (Accomodation). People with high noise have difficulty focusing on objects at all distances.
Diagnosis
It is possible to diagnose hyperopia during an ophthalmological examination, either by simply reading the characters of the optotypical table and with an in-depth instrumental investigation.
The instrumental tests most used to evaluate and characterize it are:
- theautorefractory, which provides anatomical corneal and refraction parameters,
- lo IOL-Master, which measures the length of the eyeball,
- la corneal topography, which provides some fundamental anatomical parameters analyzing the possible alterations of the corneal curvature that can give rise to hypermetropic defects,
- theB-Scan ultrasound, which evaluates in very hyperopic patients any morphological alterations inside the eye, given that the eyeball is smaller than normal and structural anomalies in the tissues could result.
How do you see a farsighted person?
If affected by this disorder, the hyperopic patient will see clearly at a distance but will have blurry vision up close. For example, as shown in the image, a patient with mild farsightedness of two diopters will see objects perfectly sharp from an infinite distance up to 50 centimeters and blurry below that distance.


Correction
Farsightedness can be corrected with concave or converging lenses, positive dioptric power. As an alternative to glasses, glasses can be used contact lenses.
Surgical Therapy
It is possible to intervene permanently thanks to the refractive surgery. There are various refractive surgery techniques, all based on modifying the curvature - and therefore the dioptric power - of the cornea, in such a way as to compensate for the refractive defect.
La photorefractive keratectomy (PRK, Photo Refractive Keratectomy) is a refractive surgery technique that has been performed for several decades to correct the refractive defect and eliminate glasses or contact lenses thanks to the use of a excimer lasers.
PRK surgery is performed under local anesthesia and lasts for a few minutes. The excimer laser allows to achieve a "vaporization" of the most superficial corneal structure, which includes the corneal epithelium, Bowman's membrane and part of the corneal stroma. Thanks to this procedure, the images are refocused on the retinal plane and the patient can see correctly again in a clear manner in a short time, without the need for glasses or contact lenses.
The technique iLASIK (Intra-Laser In Situ Keratomileusis) was developed after PRK and differs from the latter in the method of application of the excimer laser: in PRK the laser is applied to the superficial part of the cornea after removing the outermost epithelial layer, while in iLasik the laser is applied to the innermost stromal layer of the cornea thanks to the creation of a "corneal flap”, which consists of a thin layer of cornea that is made by making an incomplete circular incision with a femtosecond laser and overturning the very thin layer of cornea included inside the incision and covering the stroma.
The possibility of modeling the cornea by acting directly on the stroma allows for a immediate visual recovery e absence of pain in the postoperative period.
Both PRK and iLasik are characterized by a extremely high level of security, unrivaled in the field of eye surgery, and allow to achieve in properly selected patients results close to 100% with respect to the objectives set.
iLasik represents an evolution over PRK and has some advantages over the latter, however not all patients are suitable for this procedure. The choice of the type of refractive surgery to adopt for each specific candidate, iLasik or PRK, must be evaluated by the ophthalmologist on the basis of certain anatomical parameters of the eye.
Pathology and treatment on video
Do you need more information?
Do not hesitate to contact me for any doubt or clarification. I will evaluate your problem and it will be my concern and that of my staff to answer you as quickly as possible.




