Index
La secondary cataract it is a condition that occurs in almost all people who have undergone previous cataract surgery and consists of a fibrotic process involving the posterior capsule, the residual portion of the old natural lens, which is kept in situ to house the new artificial lens .
The process, called capsular fibrosis, determines an opacification of the tissue that contains the new artificial lens and interferes with the optical path of light inside the eye causing a blurring of vision very similar to that of a cataract. For that reason this condition is commonly called secondary cataract, albeit improperly, since the blurring of vision is not caused by the opacification of the new artificial lens – which remains perfectly transparent for life – but by the opacification of the capsule of the old natural lens.

Symptoms
The symptoms of secondary cataracts are very similar to those of cataract proper and they can appear a few months or a few years after cataract surgery. Commonly patients complain of a blurred vision very similar to the one they had before surgery and sometimes they even report glareespecially at night and in the presence of streetlights or car headlights.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of secondary cataract can be made by an examination with the slit lamp. The interference created by capsular fibrosis can be measured thanks to theinterferometry, a diagnostic technique that analyzes the path of light inside the eye; especially it IOL-Master , Pentacam AXL they give a semi-quantitative measure of the degree of opacification of the posterior capsule and of the interference this has on the passage of light inside the eye, providing useful data for evaluating when it is appropriate to intervene.
Posterior capsulotomy with YAG laser
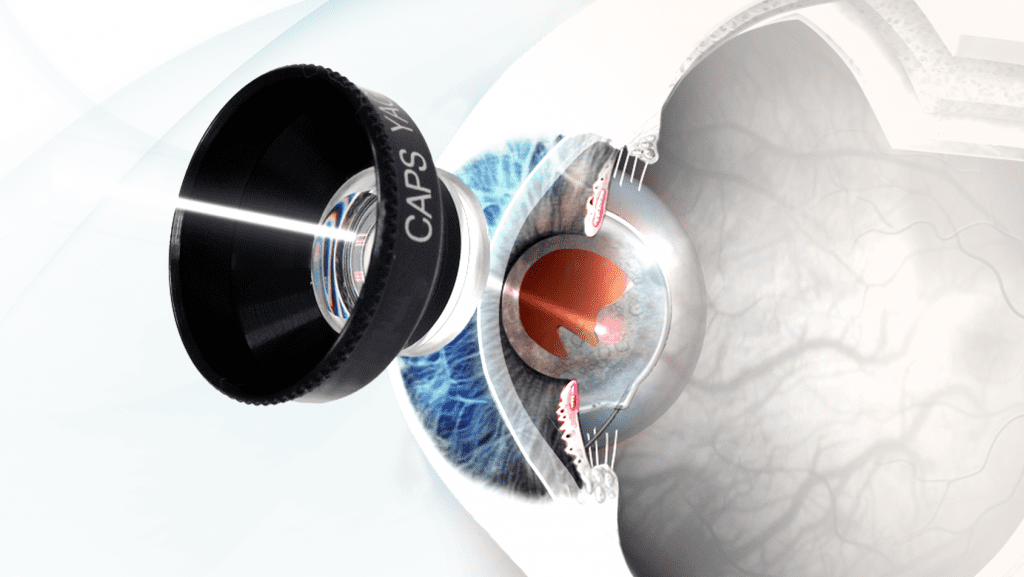
The visual impairment caused by the secondary cataract can be easily resolved thanks to a laser treatment called posterior capsulotomy with YAG laser (Yttrium Alluminium Garnet), a quick and painless procedure capable of creating a small opening in the fibrotized posterior capsule that frees the optical axis, restoring perfectly clear vision. The treatment is performed in an outpatient setting after the instillation of a local anesthetic, which allows a contact lens to be placed on the surface of the patient's cornea during the application of the laser, in the total absence of discomfort or discomfort on the part of the patient.
Once the secondary cataract is diagnosed, it is advisable not to wait too long before performing the laser capsulotomy, because in the presence of advanced fibrosis, the incision of the capsule could be more difficult and require more energy, with a greater risk of side effects.
Posterior capsulotomy with nanosecond YAG laser
Secondary cataracts can also be treated with a nanosecond YAG laser, a latest generation laser capable of emitting light radiation lasting a fraction of billionths of a second. This feature makes it possible to keep the laser energy within certain limits, making the propagation of the shock wave emitted by the laser practically impossible and eliminating the possible "domino effect", i.e. the transmission of energy from the posterior capsule to the vitreous body and following the retina.
Nanosecond YAG laser capsulotomy is a treatment that has extremely high safety and a virtually zero risk of possible side effects and complications. This is particularly important in patients with retinal diseases such as diabetic macular oedema, cystoid macular oedema, macular pucker, lamellar macular hole, vitreomacular traction (VMT) and other conditions which could be aggravated by the use of a conventional YAG laser.
Pathology and treatment on video
Answers to frequently asked questions
What is the difference between primary cataract and secondary cataract?
Primary cataract is due to opacification of the eye's natural lens, while secondary cataract is due to opacification of the posterior capsule, the tissue that houses the lens and, after cataract surgery, the artificial intraocular lens (IOL). implanted in place of the lens.
Why does secondary cataract come?
Secondary cataracts frequently occur after cataract surgery and are caused by fibrosis of the posterior capsule, the tissue that houses the natural lens and, after cataract surgery, the artificial intraocular lens (IOL) implanted in place of the lens.
What are the symptoms of secondary cataracts?
The symptoms of secondary cataracts are very similar to those of primary cataracts and consist of clouding of vision, loss of color contrast, difficulty in night vision, sometimes with the appearance of halos around lights, etc.
How is secondary cataract treated?
The visual impairment caused by the secondary cataract is eliminated by means of a laser treatment capable of creating an incision in the posterior capsule with the aim of freeing the optical path of light inside the eye.
How long does secondary cataract surgery take?
Laser surgery for secondary cataracts takes just a few minutes, but the entire procedure can last up to half an hour to prepare the eye with topical anesthetic and mydriatic eye drops.
How often can secondary cataracts be treated?
The secondary cataract appears only once in each eye, the laser treatment is definitive and does not need to be repeated.
Is secondary cataract dangerous?
Secondary cataract does not pose any risk to eye health, however the visual impairment it can create can cause risks of falls and accidents.
Do you need more information?
Do not hesitate to contact me for any doubt or clarification. I will evaluate your problem and it will be my concern and that of my staff to answer you as quickly as possible.




